Introduction
Magnesium pyrophosphate is an inorganic compound with notable applications in industries such as ceramics, detergents, and water treatment. Due to its unique properties, it serves as an essential material in various formulations, enhancing product performance and durability. This Magnesium Pyrophosphate Manufacturing Plant Project Report outlines the critical aspects of establishing a magnesium pyrophosphate manufacturing plant, covering production processes, market potential, equipment needs, and regulatory considerations.
Overview of Magnesium Pyrophosphate
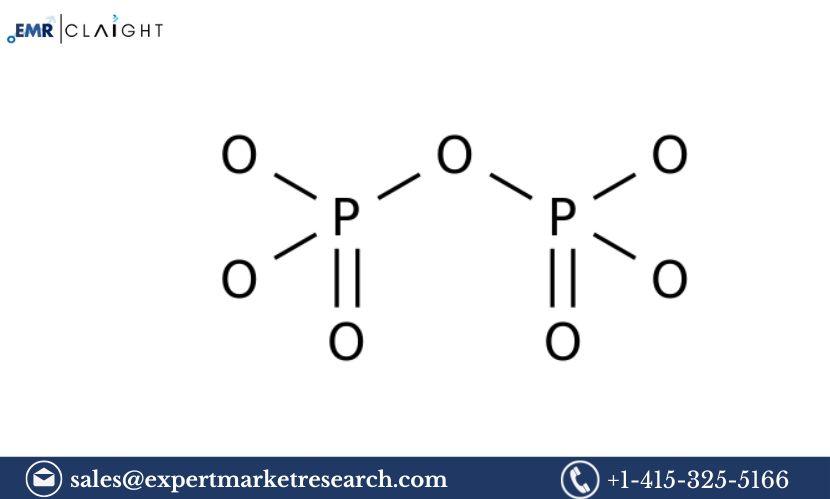
Magnesium pyrophosphate (Mg2P2O7) is known for its high thermal stability, water resistance, and excellent dispersing properties. It is widely used as a dispersing agent in ceramic glazes, detergents, and as an additive in water treatment formulations to prevent scale formation. Its ability to maintain stability under high temperatures makes it an ideal choice for various industrial applications.
Production Process of Magnesium Pyrophosphate
The synthesis of magnesium pyrophosphate involves the controlled reaction of magnesium compounds with phosphoric acid or its derivatives. Below is an outline of the typical production process:
-
Raw Material Preparation: The primary raw materials include magnesium oxide (MgO) and phosphoric acid (H3PO4). High-purity chemicals are essential for ensuring product quality.
-
Reaction and Synthesis: Magnesium oxide and phosphoric acid are mixed under controlled conditions in a reaction vessel. The mixture is heated to initiate the chemical reaction that leads to the formation of magnesium pyrophosphate.
-
Crystallization and Precipitation: The reaction mixture is cooled, allowing magnesium pyrophosphate to crystallize out of the solution. This step is carefully monitored to achieve the desired particle size and purity.
-
Filtration and Washing: The crystalline product is separated from the liquid phase using filtration techniques and washed to remove any residual byproducts or unreacted materials.
-
Drying: The purified magnesium pyrophosphate is then dried to remove excess moisture, ensuring the final product is in a stable, powder form.
-
Packaging: The dried product is packaged in moisture-resistant containers to preserve its quality during storage and transport.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@
Equipment and Infrastructure Requirements
Establishing a manufacturing plant for magnesium pyrophosphate requires specialized equipment and a well-structured facility layout:
-
Reaction Vessels: Equipped with temperature and pH control systems for precise reaction conditions.
-
Crystallization Tanks: For controlled cooling and formation of magnesium pyrophosphate crystals.
-
Filtration Units: To separate the solid product from the reaction mixture.
-
Drying Equipment: Such as rotary dryers or fluidized bed dryers to remove moisture effectively.
-
Packaging Machines: Automated systems for secure and efficient product packaging.
The facility should also incorporate safety measures like ventilation systems, fire suppression units, and spill containment to ensure a safe working environment.
Market Demand and Applications
The demand for magnesium pyrophosphate is driven by its applications in various industries:
-
Ceramics: Used as a dispersing agent in ceramic glazes to ensure a uniform consistency and enhance the durability of the final product.
-
Detergents: Serves as an additive that improves the performance of cleaning products by dispersing dirt and enhancing cleaning efficacy.
-
Water Treatment: Employed in formulations to prevent scale formation and improve the efficiency of water purification processes.
-
Construction and Adhesives: Used as a component in specialized cements and adhesive formulations for better adhesion and strength.
The global market for magnesium pyrophosphate is expected to grow as industries increasingly prioritize materials that offer superior performance and environmental benefits. This trend is supported by the push for sustainable and efficient manufacturing practices.
Financial Considerations and Investment
Establishing a magnesium pyrophosphate manufacturing plant involves significant initial and ongoing investments. Key financial considerations include:
-
Capital Expenditure (CapEx): Costs associated with land acquisition, facility construction, and purchasing equipment.
-
Raw Material Costs: Procuring high-quality magnesium oxide and phosphoric acid.
-
Operational Costs: Expenses for labor, utilities, maintenance, and quality control.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Costs related to obtaining necessary permits and ensuring compliance with safety and environmental regulations.
A detailed financial analysis should include revenue projections, cost-benefit analysis, and potential ROI to assess the plant's financial feasibility. Collaborations with industry partners and exploring government incentives for manufacturing may also contribute to financial sustainability.
Regulatory and Safety Considerations
Given the nature of chemical processing, establishing a magnesium pyrophosphate manufacturing plant requires adherence to strict regulatory and safety standards:
-
Compliance with Regulations: The plant must meet local, national, and international safety and environmental regulations. These include guidelines for chemical handling, storage, and emissions.
-
Worker Safety Protocols: Ensuring the safety of employees through training programs, the use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and emergency response protocols.
-
Environmental Impact: Implementing waste treatment systems to manage byproducts and prevent environmental contamination.
Incorporating best practices for environmental management and worker safety will help maintain a safe and compliant manufacturing environment.
Challenges and Risk Management
Several challenges can arise during the setup and operation of a magnesium pyrophosphate plant:
-
Supply Chain Reliability: Ensuring a consistent supply of raw materials can be challenging. Developing strong supplier relationships and maintaining strategic reserves can mitigate these risks.
-
Regulatory Changes: Compliance with evolving regulations may require adjustments to processes and additional investments. Staying informed through industry associations and regulatory bodies can help manage this risk.
-
Environmental Concerns: Proper waste management and emissions control are essential to prevent pollution and meet environmental standards.
Implementing risk management strategies, such as quality control checks and investing in sustainable technologies, can help reduce potential operational disruptions.
Sustainability Practices
To align with global sustainability goals, manufacturers can adopt eco-friendly practices:
-
Energy Efficiency: Utilizing energy-efficient equipment and renewable energy sources.
-
Waste Reduction: Recycling byproducts and optimizing processes to minimize waste.
-
Sustainable Sourcing: Procuring raw materials from responsible sources.
-
Community Engagement: Maintaining transparent communication with local communities and implementing practices that benefit the environment.
By integrating these sustainable practices, a magnesium pyrophosphate plant can enhance its reputation and contribute positively to environmental conservation.
FAQs
1. What are the main uses of magnesium pyrophosphate?
It is used in ceramics, detergents, water treatment, and construction materials.
2. What raw materials are needed for production?
Magnesium oxide and phosphoric acid.
3. How is product quality controlled?
Through purification, crystallization, and quality testing before packaging.
4. What safety measures should be in place?
Worker training, PPE, ventilation, fire suppression, and emergency response systems.
5. How can a plant meet environmental standards?
By implementing waste treatment systems and reducing emissions.
6. What challenges do manufacturers face?
Supply chain reliability, regulatory compliance, and environmental management.
7. What are the financial considerations for starting a plant?
CapEx, raw material costs, operational expenses, and regulatory costs.
8. What equipment is essential for production?
Reaction vessels, crystallization tanks, filtration units, and drying equipment.
9. How does magnesium pyrophosphate benefit water treatment?
It helps prevent scale formation and improves water quality.
10. What sustainable practices can be implemented?
Energy efficiency, waste reduction, sustainable sourcing, and community engagement.
This report serves as a comprehensive guide for establishing a magnesium pyrophosphate manufacturing plant, focusing on production processes, market potential, financial planning, and sustainable practices.
Related Reports
https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au/reports/australia-music-market
https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au/reports/australia-oil-and-gas-upstream-market
https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au/reports/australia-online-grocery-delivery-market
Media Contact:
Company Name: Claight Corporation
Contact Person: Lewis Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: sales@expertmarketresearch.com
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: www.expertmarketresearch.com
Aus Site: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au